What Is Frequency Modulation?
What Is Frequency Modulation?Recurrence tweak is a strategy or a course of encoding data on a specific sign (simple or computerized) by differing the transporter wave recurrence as per the recurrence of the regulating signal. As we probably are aware, a tweaking signal is only data or message that must communicated subsequent to changed over into an electronic sign.Similar as sufficiency balance, recurrence regulation likewise has a comparative methodology, where a transporter signal is tweaked by the info signal.
Nonetheless, on account of FM, the adequacy of the balanced sign is kept, or it stays consistent.The recurrence tweak list is for the most part more than 1, and it normally requires a high data transfer capacity at a scope of 200 kHz. FM works in an extremely high-recurrence range, typically between 88 to 108 Megahertz. There are mind boggling circuits with an endless number of sidebands that assistance in getting great signs with high sound quality.
Broadcast stations in the VHF portion of the frequency spectrum between 88.5 and 108 MHz often use large values of deviation (±75 kHz). This is known as wide-band FM (WBFM). Even though these signals support high-quality transmissions, they do occupy a large amount of bandwidth. Normally, 200 kHz is allowed for each wide-band FM transmission. On the other hand, communications use very little bandwidth. Whereas narrowband FM (NBFM) often uses deviation figures of around ±3 kHz. Besides, narrow-band FM is mostly used for two-way radio communication applications.
Assuming
we discuss the utilizations of recurrence tweak, it is for the most part utilized in radio telecom. It offers an extraordinary benefit in radio transmission as it has a bigger transmission to-commotion proportion, and that implies that it brings about low radio recurrence obstruction. This is the principal reason that many radio broadcasts use FM to communicate music over the radio.Furthermore, a portion of its purposes are likewise tracked down in radar, telemetry, seismic prospecting, and in EEG, different radio frameworks, music union as well as in video-transmission instruments. In radio transmission, recurrence tweak enjoys a decent upper hand over other balance. It has a bigger transmission to-clamor proportion, meaning it will dismiss radio recurrence obstructions far superior to an equivalent power plentifulness regulation (AM) signal. Because of this significant explanation, most music is communicated over FM radio.
FM Modulators
What Is Frequency Modulation?There are a few strategies that can be utilized to produce either immediate or circuitous recurrence tweaked signals.
A voltage-controlled oscillator or varactor diode oscillator: A voltage-controlled oscillator can utilized to shape direct FM regulation by straightforwardly taking care of the message into the contribution of the oscillator. On account of the varactor diode, we place this gadget inside the tuned circuit of an oscillator circuit.
stone oscillator circuit wherein the sign should be duplicated in recurrence, and just narrowband FM is accomplished.
Stage locked circle: This is an amazing technique to produce recurrence adjustment signals. Be that as it may, the requirements inside the circle ought to checked cautiously, and when everything is steady, it offers a magnificent arrangement.
Frequency Modulation Equations
Recurrence balance conditions principally comprise of a sinusoidal articulation with the fundamental of the baseband signal that can be either a sine or cosine capability.
It very well may be addressed numerically as;
m(t) = Am cos (ωmt + Ɵ) … … … … … … 1
m(t) → adjusting signal
Where,
Am → Abundancy of the adjusting signal.
ωm → Precise recurrence of the adjusting signal.
Ɵ → It is the period of the balancing signal.
Same as sufficiency balance, when we attempt to regulate an info signal (data), we really want a transporter wave, and we will insight
C(t) = ac cos (ωct + Ɵ) … … … … .. 2
Precise adjustment, and that implies ωc (or) Ɵ of the transporter wave, begins shifting straightly concerning the tweaking signal, similar to plentifulness balance.
Likewise Read: Correspondence Frameworks
Case I: Any Moment
The tweaking signal at any moment of time.
C(t) = ac cos (ωct + Ɵ)
For a specific moment (ωct + Ɵ) isn’t fluctuating regarding time the Ɵ turns out to be so it Ɵ0 = consistent, then, at that point,
ωc = additionally steady
On the off chance that we draw a digression for the given sign at any moment of time, the slant of the digression gives ωc, and the digression, when it cuts the Ɵ-hub, gives Ɵ0 esteem.
Case II: For a Little Timespan
Presently, let us think about a little timespan Δt = t2 – t1
Time span, t1 < t < t2, we will look this into two specific moment of t1 and t2
Allow us to consider a moment at (t1); in the event that we attract a digression to a given sign at (t1), the slant of the bend prompt recurrence (wi) at that specific moment.
Essentially, the catch of the digression with Ɵ – hub gives the prompt stage (Ɵi). Moreover, we can get wi for any moment of the given bend. From this, one thing is clear,
Ɵ – is the stage at the moment
We compose this as a component of time (t), and momentary recurrence is
k – consistent
ωc → recurrence of the transporter wave
m(t) → balancing signal
The addition signal in this stage becomes,
A cos Ɵ (t) = ac cos [ωct + k m(t)]
Assuming we really want the recurrence of the wave,
ωc + km(t) … … … .6 [this is known as recurrence modulation]
Where,
Assuming we really do stage regulation, it is only recurrence adjustment. At the point when we do recurrence regulation, we are separating the specific adjusting signal, which then consequently portrays it as stage tweak.
Expression for Frequency Modulated Wave
AS we Know
are aware, from plentifulness regulation, we really want two sine (or) cosine waves for balance.
m(t) = Am cos (ωmt) and
c(t) = ac cos (ωct)
or then again
m(t) = Am cos (2π fmt)
c(t) = ac cos (2πfct)
Then, at that point, recurrence balanced wave will be:
fm(t) = fc + k Am cos (2π fm t )
fm (t) = fc + k m(t)
Where,
fm(t) = recurrence adjusted wave
fc → recurrence of the transporter wave
m(t) → adjusting signal
k → proportionality consistent
c
In FM, variety (or) deviation in recurrence, the greatest deviation is Δfmax
Δfmax = │fm(t) – fc│
=│KAm cos(2π fmt) │
The greatest deviation in recurrence is K Am
By and large, recurrence deviation characterized as the proportion of the adjustment of a transporter recurrence delivered by the sufficiency of the info tweaking signal
Modulation Index (μ)
The balance list is the proportion of most extreme deviation in recurrence of the tweaking signal.
Additionally Read: Contrasts among AM and FM
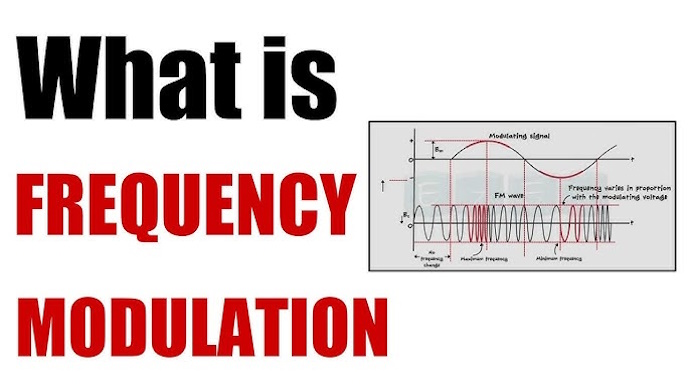
Graphical Representation of Frequency Modulated Wave
In the event that we notice the chart, we can see that the recurrence of a transporter increments when the plentifulness of the information signal expanded. Here, the transporter recurrence is greatest when the information signal is at its most noteworthy. Likewise, the recurrence of a transporter diminishes in the event that the plentifulness of the balancing signal goes down. What it implies is that the transporter recurrence is least when the information signal is at its most reduced.
Frequency Demodulation
At the point when there is regulation, ordinarily, we want to effectively demodulate it and, simultaneously, recuperate the first sign. In such cases, a FM demodulator, otherwise called a FM discriminator or FM identifier, utilized. While there are a few sorts of FM demodulators, the primary usefulness of these gadgets is to change over the recurrence varieties of the info signal into plentifulness varieties of the result signal. The demodulators utilized alongside a sound intensifier or conceivably a computerized interface.
Amplitude Modulation vs Frequency Modulation
While FM and AM capability likewise, the principal contrast lies in how their transporter waves adjusted. On account of AM, the sign strength shifts to consolidate sound data, while for FM, the recurrence at which ongoing heads in a different path each second for the transporter signal changed. We will take a gander at a portion of the distinctions among FM and AM belo
Frequently Asked Questions on Frequency Modulation
Q1How does frequency modulation work?
The encoding of data in a transporter wave by changing the wave’s quick recurrence known as recurrence regulation (FM). FM innovation is every now and again utilized in the fields of registering, broadcast communications, and sign handling.
Q2What is the advantage of frequency modulation over amplitude modulation?
The encoding of data in a transporter wave by changing the wave’s immediate recurrence known as recurrence balance (FM). FM innovation habitually utilized in the fields of registering, broadcast communications, and sign handling.
Q3How is the process of frequency modulation done?
The recurrence of the radio transporter changed as per the plentifulness of the approaching sound stream to shape a recurrence balanced signal.
Q4What are the different types of analog modulation systems?
Recurrence Balance, Adequacy Adjustment, and Stage Regulation are the various sorts of nonstop wave simple tweak frameworks, while PAM, PWM and PPM are the beat simple balance frameworks.
Q5What is frequency modulation?
Recurrence adjustment is the strategy for changing the transporter sign’s momentary recurrence as per the message sign’s prompt abundancy.
Q6List the uses of modulation.
Regulation has the accompanying purposes.
Diminishes radio wire level.
Evades signal blending.
Increments correspondence range.
Multiplexing is conceivable.
Further develops gathering quality.
Q7What is frequency deviation?
The FM signal’s instantaneous frequency changes with time around the carrier frequency ωc. This indicates that the FM signal’s immediate frequency varies depending on the modulating signal. Frequency deviation is the maximum change in instantaneous frequency from the average frequency ωc.
Q8What are the drawbacks of frequency modulation over amplitude modulation?
In FM broadcasting, an essentially more extensive channel required, roughly 200 kHz, contrasted with just 10 kHz in AM communicating. This is a huge limitation of FM. FM sending and getting hardware, particularly used for adjustment and demodulation, is more confounded and accordingly more costly.