Ever wondered how an oven turns cold dough into delicious baked goods? Whether you’re new to cooking or just curious, understanding how an oven works can improve your results in the kitchen — and help you choose the right appliance.
This article explains how ovens work, their heating mechanisms, and the differences between types of ovens, using easy-to-understand language and SEO-friendly content.
🔥 What Is an Oven?
An oven is a kitchen appliance used to cook, bake, roast, or heat food. It generates controlled heat in a closed chamber to prepare meals evenly from all sides.
There are various types of ovens, but they all follow the same basic principle: convert energy (electricity or gas) into heat and distribute it within an insulated space.
⚙️ How Does an Oven Work?
Here’s a simple breakdown of how an oven functions:
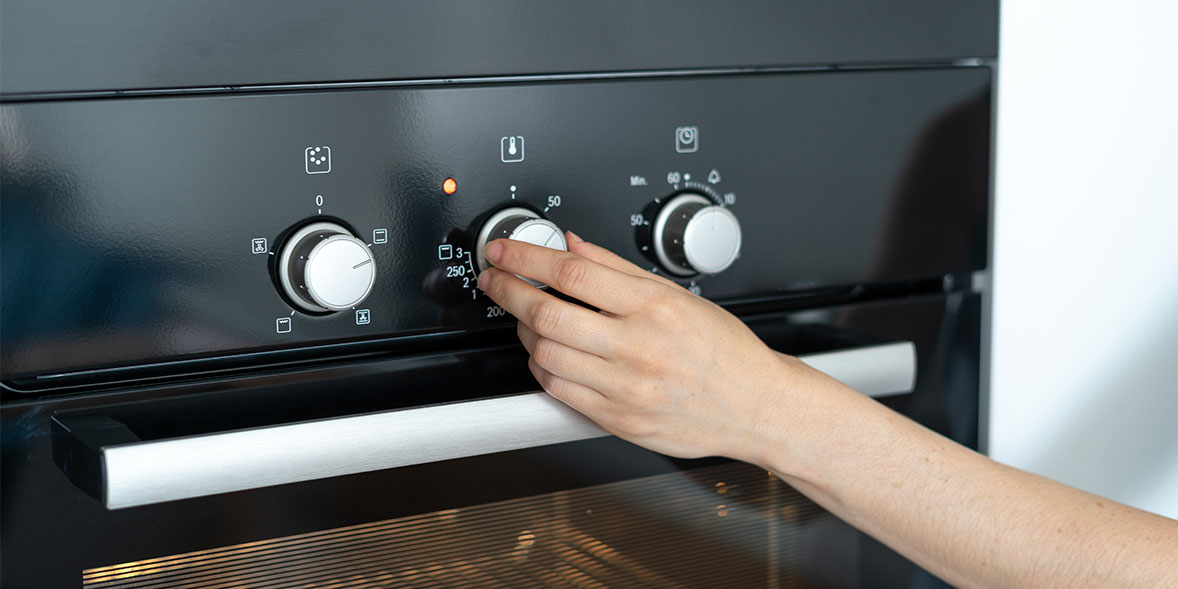
1. Heat Generation
Ovens generate heat using either:
- Electric heating elements (in electric ovens)
- Gas burners (in gas ovens)
When you turn the oven on and set a temperature, the heat source activates and starts warming the oven interior.
2. Temperature Control
Modern ovens use thermostats or temperature sensors to:
- Maintain consistent heat
- Turn the heating element on/off
- Prevent overheating or underheating
This ensures even cooking and avoids burning your food.
3. Heat Distribution
Heat inside an oven is spread in different ways depending on the type of oven:
- Conventional ovens: Heat rises naturally; top of the oven is hotter.
- Convection ovens: A built-in fan circulates hot air evenly.
- Microwave ovens: Use electromagnetic waves to heat food molecules.
- Toaster ovens: Use small electric coils for direct heating.
🧑🍳 Types of Ovens and How They Work
Let’s break down the major oven types and their heating systems:
🔌 Electric Ovens
- Use metal coils (top and bottom) that heat up when electricity passes through.
- Heat is distributed naturally or with a fan (in convection models).
- Known for precise temperature control.
🔥 Gas Ovens
- Use burners fueled by natural gas or LPG.
- Heat rises from a flame at the bottom.
- May have uneven heating without a fan.
🌬️ Convection Ovens
- Include a built-in fan and exhaust system.
- Distribute heat evenly — great for baking, roasting, and crisping.
- More energy-efficient and faster cooking than traditional ovens.
⚡ Microwave Ovens
- Use microwaves (radio waves) to excite water molecules inside food.
- Heats food from the inside out.
- Best for reheating, not ideal for baking.
🔥 Toaster Ovens
- Small countertop ovens with electric heating elements.
- Combine features of ovens and toasters.
- Ideal for small meals, snacks, or reheating.
🔎 How Oven Heat Affects Cooking
- Dry Heat (electric/gas ovens): Creates a crispy, browned texture — perfect for baking bread, roasting meat, and broiling.
- Even Circulation (convection): Prevents undercooked spots and reduces cooking time.
- Moisture Retention (microwave): Retains food moisture but lacks browning.
💡 Oven Maintenance Tips
- Always preheat your oven before baking.
- Clean spills and food debris regularly.
- Use oven-safe cookware only.
- Test temperature accuracy with an oven thermometer.
📌 Final Thoughts
Understanding how ovens work helps you become a smarter, more confident cook. Whether you’re using a gas oven, electric model, or convection type, each one has its own benefits. Choose the right oven based on your cooking style, and you’ll enjoy better results — and tastier food!
Powered By: https://mraalionline.com