Introduction
In recent days, reports have swirled around a purported U.S.-backed “peace plan” aimed at resolving the war in Ukraine. According to media outlets, this plan includes sweeping diplomatic, security, and territorial proposals. But in a carefully worded response, the Kremlin declared that it has not received anything official from Washington. This declaration is not merely procedural. It’s a strategic signal. As Moscow frames its response, it underscores how fraught diplomatic efforts remain, even as Western capitals debate whether to restart negotiations or press for a military victory.
In this article, we explore what exactly has been reported about the U.S. peace plan, why the Kremlin’s position matters, how Kyiv and its Western allies are responding, and what scenarios might emerge next. We assess long term implications for European security, international norms, and the future of Russia Ukraine relations.
Background: Reports of a U.S. Peace Plan
Over the last week, multiple media outlets have reported that Washington has drafted a detailed peace proposal, reportedly consisting of dozens of points. According to these reports, the plan would require Ukraine to make substantial concessions: recognizing certain territories as part of Russia, agreeing to restrictions on its defense posture, and possibly forgoing its ambitions to join NATO. In return, the United States and its allies would offer various security guarantees, economic incentives, and perhaps a roadmap for phased sanctions relief.
While the details of the plan remain largely unconfirmed by official documents, the leaks attributed to both U.S. And Ukrainian sources suggest a high stakes diplomatic gambit. For the United States, supporters argue. This plan could be a way to finally end a war that has strained U.S. resources and global reputation. For Kyiv, the leaks raise profound questions. Is this a genuine pathway to peace, or a disguised capitulation?
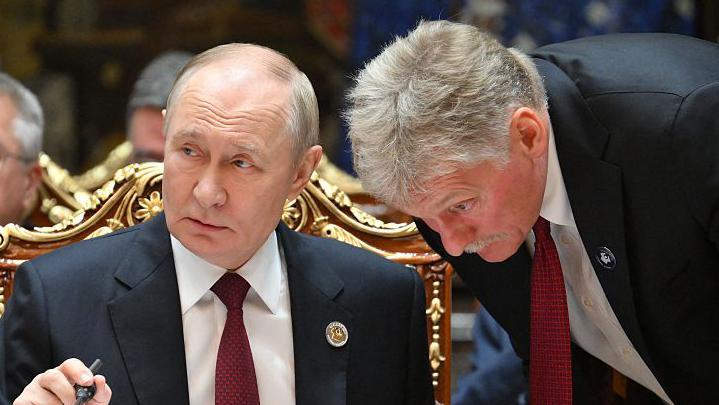
Moscow’s Rejection: “Nothing Official”
In response to media coverage, the Kremlin, via its spokesperson, announced that Russia has not received any formal proposal from the United States. According to Russian officials, while they have seen some “ideas” circulating in the press. No official diplomatic instrument no written draft, no notes verbals , no treaty text has been presented. Moreover, Moscow claims there has been no “substantive discussion” with Washington on the specifics of the plan.
This carefully calibrated response performs several tactical functions:
- Buys Time: By asserting that nothing formal has been delivered, Moscow delays commitment. It avoids being boxed into a public yes or no, preserving room to maneuver.
- Preserves Leverage: If a plan is still in draft form or preliminary, Russia can influence the text in later rounds. By withholding acknowledgement, Moscow retains bargaining power.
- Signals Cautious Openness: While denying receipt, the Kremlin also describes itself as “open” to negotiations. That keeps the door ajar diplomatically, without making concessions.
- Shifts Pressure Back to Kyiv: By saying Kyiv could be running out of negotiating space due to territorial changes on the ground, Moscow subtly warns Ukraine that continued fighting may strengthen Russia’s hand.
Why Moscow’s Ambiguity Matters
Moscow’s declaration is more than bureaucratic nicety. It’s a calculated diplomatic posture. Here’s why it matters:
- Psychological Warfare: Publicly asserting non-receipt weakens the narrative that the United States has already made Russia a generous offer. It undermines any image of U.S. magnanimity and reframes it as media sensation rather than diplomatic reality.
- Projection of Strength: By neither rejecting nor accepting, Russia projects confidence. It conveys that it is not desperate for peace and that the initiative, if real, must meet its terms.
- Battlefield Correlation: With its military still pressing on several fronts, Moscow can use its ambiguous line to maintain operational tempo. If Ukraine believes a deal is imminent, it may halt advances, but Russia’s standing gives it freedom to push or pause as needed.
- Internal Legitimacy: Domestically, this posture lets the Kremlin tell its people that it will not make concessions under pressure. Any eventual deal can be spun as a negotiated victory rather than a forced compromise.
Kyiv’s Response: Cautious Engagement
Kyiv’s reaction has been delicately balanced. Ukrainian leaders acknowledge that they have seen drafts of a potential peace proposal. However, they insist that any agreement must safeguard Ukraine’s sovereignty, preserve its right to self-defense, and avoid setting precedents that reward aggression.
Key elements in Kyiv’s position include:
- Skepticism Over Leaks: Ukrainian officials caution that media leaks may not reflect a fully baked, officially sanctioned U.S. plan. Some believe the leaks could be a trial balloon, intended to test public opinion or put pressure on Kyiv.
- Insistence on “Dignified Peace”: Kyiv emphasises that any negotiated deal must be acceptable to the Ukrainian people, and not imposed from above. Ukrainian leaders stress that peace without justice . Without full restoration of territory or respect for Ukraine’s right to choose its alliances would a hollow victory.
- Coordination with Allies: Kyiv has called for stronger coordination with European allies, NATO, and individual donor nations, rather than relying on a bilateral U.S.-Russia framework. For Ukraine, a multilateral deal ensures greater guarantees and oversight.
Allied Reaction: Concern Over Process
European capitals have expressed unease at how this proposed peace plan is emerging. Their concerns are not purely about content many share Kyiv’s fear of rewarding territorial conquest. But also about process. Key worries include:
- Lack of Allied Consultation: Some European leaders feel blindsided if Washington is advancing a framework before fully coordinating with its European partners. This could undermine transatlantic unity and weaken collective leverage over both Kyiv and Moscow.
- Precedent Risks: European states are wary that a deal granting territorial recognition without a just peace would set a dangerous precedent for other conflicts in Europe or elsewhere.
- Accountability and Enforcement: There are doubts about how any deal would be enforced. Without robust monitoring, verification, and penalty mechanisms, an agreement could quickly unravel.
- Sanctions Leverage: If sanctions relief is part of the package, European capitals worry that easing sanctions too early could undermine Ukraine’s negotiating leverage and reward aggression.
Underlying Motives: Why the U.S. Might Be Pushing a Plan
Why would Washington promote a peace plan now, particularly one that may require Ukraine to cede significant ground? Several overlapping motivations may explain:
- War Fatigue: Supporting Ukraine militarily has come at great cost to the U.S. and its allies. After years of war, a diplomatic solution may appear more attractive than an open-ended commitment.
- Domestic Politics: U.S. policymakers may be under pressure to produce a breakthrough. A peace initiative gives political cover, even if a deal never materializes.
- Strategic Reset: The U.S. may see a deal as a way to re-shape European security architecture in a way that preserves long-term interests, even if it requires short-term compromise.
- Containment of Russia: Rather than achieving total defeat, the U.S. might aim for a managed detente . A framework that locks in some strategic limits on Russia while preventing further escalation.
- Leverage for Sanctions: A potential deal gives Washington bargaining chips: offer relief in exchange for commitments, or threaten to withhold support.
Risks and Challenges for Ukraine
For Ukraine, the stakes could not be higher. Accepting a peace deal under these reported terms could jeopardize national integrity, security, and long-term strategic interests. Key risks include:
- Territorial Losses: Recognizing areas now held by Russia could permanently strip Ukraine of critical regions, undermining its national identity and economic potential.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Limiting its military or pledging neutrality could leave Ukraine exposed to renewed aggression.
- Erosion of Sovereignty: If decisions about Ukraine’s future are mediated significantly by the U.S. and Russia, Kyiv may lose agency over crucial choices.
- Domestic Backlash: Ukrainian public opinion is deeply invested in national sovereignty. Any perception of compromise could provoke strong political resistance.
- Weak Guarantees: Without ironclad verification and enforcement, promises of security or sanctions relief might not materialise in the long run.
Risks and Challenges for Russia
While Moscow might benefit from a favourable deal, it also faces risks. Key challenges include:
- Sanctions Relief Uncertainty: Even if some sanctions are lifted, the economic and political costs of reintegration in the West remain high.
- Domestic Expectations: The Kremlin must deliver a narrative of victory. If a deal is perceived domestically as a compromise, it could weaken Putin’s legitimacy.
- Strategic Overreach: Demanding too much from Kyiv could backfire, destabilizing occupied territories or prompting renewed resistance.
- Long-Term Security Commitments: Russia may be asked to enter into complex security guarantees. If not carefully managed, this could limit its freedom of action.
- Compliance Pressure: Any formal treaty could expose Russia to international mechanisms (monitoring, inspections), which Moscow may find constraining.
Possible Scenarios Moving Forward
Given the complexities, several potential scenarios could play out in the coming weeks and months:
- Formal Transmission of a Written Proposal
The U.S. could officially pass a written draft to Russia. Moscow might then issue a detailed response, starting formal negotiations. This could lead to a high-risk bargain: Ukraine may make painful concessions, but peace could be achieved — though potentially fragile. - Negotiations Stall or Collapse
Without full alignment among Western allies, or if Ukraine rejects the terms, the plan could collapse. Russia’s “not received officially” line may prove durable cover for a return to fighting. In this case, diplomatic momentum might break, and we’d see renewed escalation on the battlefield. - Interim Truce, Followed by Consolidation
A limited ceasefire might emerge first, tied to localized troop withdrawals or confidence-building measures. Russia could use any lull to fortify positions, rebuild, and press for a better long-term deal later. This scenario risks being a strategic pause rather than a real resolution. - Fragmented Diplomatic Outcomes
A patchwork settlement might develop, with some regional powers or third-party states endorsing separate deals. Western unity could fracture, leaving Ukraine exposed and Russia partially legitimized. This version risks creating a “gray zone” of contested authority and future instability. - Back-Channel Diplomacy Only
Even without public acknowledgment, back-channel negotiations could intensify quietly. Moscow and Washington might work through intermediaries, avoiding direct public confrontation. If that happens, any deal could be donned with layers of secrecy — increasing mistrust and reducing transparency.
Long-Term Implications
If some version of a peace agreement emerges, its impact could reshape Europe’s security architecture and global diplomacy. Here are some of the most significant consequences:
- Precedent for Territorial Realignment
Recognizing wartime territorial changes could weaken international norms against conquest, emboldening other revisionist states. A deal that treats occupation as legitimate settlement has broad geopolitical risk. - Reconfiguration of NATO and European Security
A settlement could lead to new security arrangements in Eastern Europe, possibly tying Ukraine into a neutral status or granting it limited defense rights. The role of NATO and its posture could become deeply contested. - Sanctions Regimes and Economic Realignment
Phased sanctions relief could help Russia re-enter global financial and commercial systems — but also anger states that view economic pressure as critical leverage. The balance between accountability and reconciliation would be contentious. - Peace Durability and Enforcement
Without strong verification mechanisms, any ceasefire or peace treaty could collapse. Monitoring, institutions, and guarantees would be vital to preventing recurrence of conflict. - Domestic Political Fallout in All Capitals
Leaders who negotiate hard compromises may face internal backlash. In Ukraine, loss of territory or security could provoke political revolt. In Russia, a deal perceived as insufficient might weaken the Kremlin’s narrative of triumph. In the U.S. and Europe, public opinion could swing sharply depending on perceived success or failure. - Global Diplomatic Lessons
The way Washington handles this plan could influence how future great-power conflicts are mediated. If the U.S. is seen to offer major concessions without allied consensus, trust in its diplomacy could suffer. Conversely, a well-structured, multilateral peace process could strengthen international institutions.
Why the “Not Received” Line Is Important Now
Moscow’s insistence that it has not received anything official is not a mere technicality. It highlights several deeper dynamics:
- Negotiation Stage: The peace proposal appears still in a very preliminary phase. The public discussion may outpace the actual diplomatic exchange.
- Information Strategy: Russia is using media reports to shape its own bargaining narrative. By treating leaks as non-official, Moscow can deny commitments while simultaneously signalling interest.
- Strategic Posturing: Moscow is underlining that it is not bargaining from weakness. It wants to appear strong, composed, and unwilling to rush into a suboptimal deal.
- Bargaining Leverage: By not confirming receipt, Russia retains maximum leverage to influence a future text or reject one that doesn’t meet its objectives.
The Human and Moral Stakes
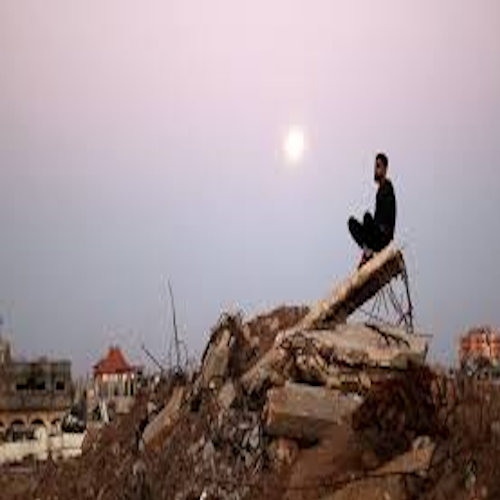
Beyond great-power politics, the human cost of this conflict remains staggering. Millions of Ukrainians have endured displacement, loss of life, and destruction of their homes. Any peace plan must reckon with humanitarian realities: rebuilding infrastructure, resettling displaced people, ensuring justice for war crimes, and protecting minority rights.
If a deal is reached, crafting a durable, just peace will require far. More than territorial swaps and security guarantees. It will necessitate:
- Reconstruction Mechanisms: Massive investments in rebuilding war-torn communities, rebuilding cities, and reviving economies.
- Transitional Justice: Mechanisms for accountability, including prosecutions, truth commissions, or reparations.
- Refugee Return Frameworks: Safe, voluntary, and dignified return paths for refugees and internally displaced persons.
- Civil Society Inclusion: Ensuring that peace is not solely driven by governments, but includes input from local communities, civic organisations, and ordinary citizens.
- Long-term Institutional Reform: Strengthening governance structures, transparency, and human rights protections to prevent renewal of conflict.
Policy Lessons for Global Actors
From this unfolding episode, several crucial lessons emerge for governments and international organisations:
- Transparency Matters: Leaks and back-channel proposals can undermine trust. Formal diplomatic transmission is essential — not just for legitimacy, but for real negotiation.
- Allied Coordination Is Key: Major peace efforts must involve key stakeholders from the outset. Marginalizing allies risks fracturing unity and weakening enforcement.
- Security Guarantees Must Be Credible: Any deal must include robust, verifiable security guarantees backed by real institutions or alliances.
- Humanitarian Priorities Cannot Be Secondary: A lasting peace must address not just military issues but also reconstruction, justice, and social healing.
- Domestic Politics Shape Outcomes: Peace negotiators must engage with their own publics — without domestic legitimacy, even the best deal may fall apart.
- Adaptive Diplomacy: Given the fluidity of modern war, plans must remain flexible and phased. A rigid, all-or-nothing treaty is riskier than a step-by-step framework with built-in review.
Conclusion
Russia’s public insistence that it has not received anything official from the U.S. on a so-called peace plan is more than a passing diplomatic nuance . It is a purposeful strategy. At a moment when powerful capitals may be seeking. A way out of a protracted war, Moscow is signaling. It will not rushed, will not boxed in. And retains significant bargaining power.
For Ukraine, the potential deal presents both opportunity and existential risk. A settlement could bring desperately needed peace and reconstruction, but only if Kyiv can secure terms that preserve its sovereignty, security, and dignity. For European allies, there is a delicate balancing act between supporting a negotiated resolution and ensuring that any agreement does not reward aggression or weaken long-term deterrence.
Ultimately, the fate of this proposal , whether it fades into another failed diplomatic gambit or marks a turning point , will depend not only on. What Moscow and Washington do next, but on how Ukrainian leaders. European capitals, and the broader international community respond. Whatever happens, the “not received officially” line underscores. That, for now, the war’s resolution remains far from guaranteed.
Related Article :
A Comprehensive Overview On US Support Programs
Tragedy in Balochistan: The Heartbreaking Murder of Bano and Ehsan